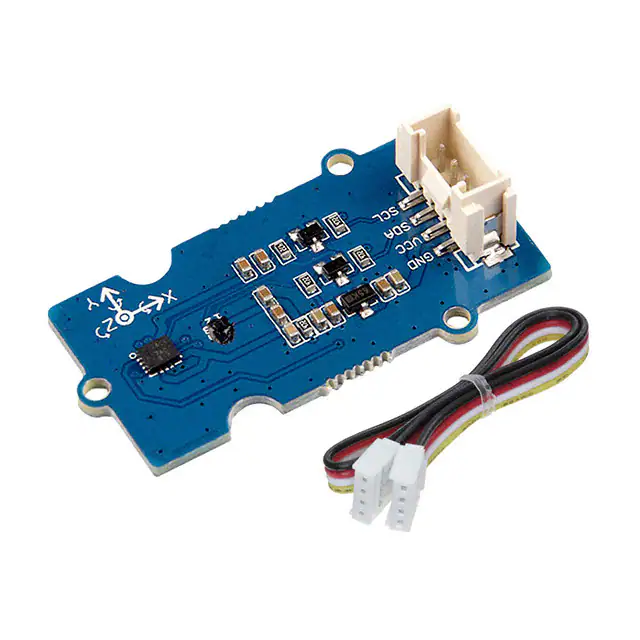
Grove - IMU 9DOF(lcm20600+AK09918)
The Grove - IMU 9DOF (lcm20600+AK09918) is a 9 Degrees of Freedom IMU (Inertial
measurement unit) which combines gyroscope, accelerometer and electronic compass.
We use two chips LCM20600+AK09918 to implement those 3 functions.
The LCM20600 is a 6-axis MotionTracking device that combines a 3-axis gyroscope, 3axis accelerometer. Gyroscope is a device used for measuring or maintaining
orientation and angular velocity, normally, we use it to measure spin and
twist. Accelerometer is a device that measures proper acceleration.
The AK09918 is a 3-axis electronic compass IC with high sensitive Hall sensor
technology. We use an electronic compass to measure the magnetic force, which can
provide us with the direction information.
�
As its name suggests just use this single small module and you can measure 9 Degrees
of Freedom: angular rotation in x/y/z axis, acceleration in x/y/z axis, and magnetic force
in x/y/z axis.
What an amazing module! Just use this module to build your own motion and
orientation system😄
Features
3-Axis Gyroscope with Programmable FSR of ±250 dps, ±500 dps, ±1000 dps, and ±2000
dps
3-Axis Accelerometer with Programmable FSR of ±2g, ±4g, ±8g, and ±16g
3-Axis Electronic Compass with 0.15 μT/LSB (typ.) sensitivity
User-programmable interrupts
16-bit ADC resolution and Programmable Filters for acceleration measurements
16-bit ADC resolution for magnetic measurements
1 KB FIFO buffer enables the applications processor to read the data in bursts(LCM20600)
Embedded temperature sensor
Magnetic sensor overflow monitor function
Built-in oscillator for internal clock source
Specification
Item
Value
Operating voltage
3.3V / 5V
Operating temperature
‐30°C to +85°C
Gyroscope Full‐Scale Range
±250 dps, ±500 dps, ±1000 dps, ±2000 dps
Gyroscope Sensitivity Scale Factor
131 LSB/(dps)@±250 dps
65.5 LSB/(dps)@±500 dps
32.8 LSB/(dps)@±1000 dps
16.4 LSB/(dps)@±2000 dps
Accelerometer Full‐Scale Range
±2g, ±4g, ±8g, ±16g
Accelerometer Sensitivity Scale Factor
16384 LSB/g@±2g
8192 LSB/g@±4g
4096 LSB/g@±8g
2048 LSB/g@±16g
�
Item
Value
Magnetic sensor measurement range
±4912μT (typical)
Magnetic sensor sensitivity
0.15μT (typical)
Interface
I2C
I2C Address
LCM20600
0x69(default)
0x68(optional)
AK09918
0x0C
Applications
Smartphones and Tablets
Wearable Sensors
Hardware Overview
Pin Out
�
Danger
The default I2C address of LCM20600 is 0x69, you can change it to 0x68. The central
pad is connected to the address wire, you can change the I2C address by cutting the
wire and re-welding it. For the safety of you and others, please be careful with knife or
welding gun you may use.
Schemaitc
Power
�
Since the operating voltage range of LCM20600 is 1.71V to 3.45V, and the operating
voltage range of AK09918 is 1.65V to 1.95V, we use a power conversion
chip XC6206P182MR to provide a stable 1.8V for both chips.
Bi-directional level shifter circuit
This is a typical Bi-directional level shifter circuit to connect two different voltage section
of an I2C bus. The I2C bus of two chips use 1.8V, if the I2C bus of the Arduino use 5V or
3.3V, this circuit will be needed. In the schematic above, Q1 and Q2 are N-Channel
MOSFET CJ2102, which act as a bidirectional switch. In order to better understand this
part, you can refer to the AN10441
Platforms Supported
Arduino
Raspberry Pi
BeagleBone
Wio
LinkIt ONE
Caution
The platforms mentioned above as supported is/are an indication of the module's
hardware or theoritical compatibility. We only provide software library or code examples
for Arduino platform in most cases. It is not possible to provide software library / demo
code for all possible MCU platforms. Hence, users have to write their own software
library.
�
Getting Started
Play With Arduino
Hardware
Materials required
Seeeduino V4.2
Base Shield
Grove ‐ IMU 9DOF
Note
1 Please plug the USB cable gently, otherwise you may damage the port. Please use
the USB cable with 4 wires inside, the 2 wires cable can't transfer data. If you are not
sure about the wire you have, you can click here to buy
2 Each Grove module comes with a Grove cable when you buy. In case you lose the
Grove cable, you can click here to buy.
Step 1. Connect the Grove - IMU 9DOF (lcm20600+AK09918) to port I2C of GroveBase Shield.
Step 2. Plug Grove - Base Shield into Seeeduino.
Step 3. Connect Seeeduino to PC via a USB cable.
�
Note
If we don't have Grove Base Shield, We also can directly connect this module to
Seeeduino as below.
Seeeduino
Grove ‐ IMU 9DOF
5V
Red
GND
Black
SDA
White
SCL
Yellow
Software
Note
If this is the first time you work with Arduino, we strongly recommend you to see Getting
Started with Arduinobefore the start.
Step 1. Download the Grove - IMU 9DOF (lcm20600+AK09918) Library from
Github.
Step 2. Refer to How to install library to install library for Arduino.
Step 3. Restart the Arduino IDE. Open the example, you can open it in the following
three ways:
a. Open it directly in the Arduino IDE via the path: File → Examples → Grove
IMU 9DOF ICM20600 AK09918 → compass.
�
b. Open it in your computer by click the compass.ino which you can find in the
folder XXXX\Arduino\libraries\Seeed_ICM20600_AK09918master\examples\compass, XXXX is the location you installed the Arduino
IDE.
c. Or, you can just click the icon
in upper right corner of the code block to copy
the following code into a new sketch in the Arduino IDE.
1#include "AK09918.h"
2#include "ICM20600.h"
3#include
4
5AK09918_err_type_t err;
6int32_t x, y, z;
7AK09918 ak09918;
8ICM20600 icm20600(true);
9int16_t acc_x, acc_y, acc_z;
10int32_t offset_x, offset_y, offset_z;
11double roll, pitch;
12// Find the magnetic declination at your location
13// http://www.magnetic-declination.com/
14double declination_shenzhen = -2.2;
15
16void setup()
17{
18 // join I2C bus (I2Cdev library doesn't do this automatically)
19 Wire.begin();
20
21 err = ak09918.initialize();
22 icm20600.initialize();
23 ak09918.switchMode(AK09918_POWER_DOWN);
24 ak09918.switchMode(AK09918_CONTINUOUS_100HZ);
25 Serial.begin(9600);
26
27 err = ak09918.isDataReady();
28 while (err != AK09918_ERR_OK)
29 {
Serial.println("Waiting Sensor");
30
delay(100);
31
err = ak09918.isDataReady();
32
33 }
34
35 Serial.println("Start figure-8 calibration after 2 seconds.");
36 delay(2000);
37 calibrate(10000, &offset_x, &offset_y, &offset_z);
38 Serial.println("");
39}
40
41void loop()
42{
�
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97}
98
// get acceleration
acc_x = icm20600.getAccelerationX();
acc_y = icm20600.getAccelerationY();
acc_z = icm20600.getAccelerationZ();
Serial.print("A: ");
Serial.print(acc_x);
Serial.print(", ");
Serial.print(acc_y);
Serial.print(", ");
Serial.print(acc_z);
Serial.println(" mg");
Serial.print("G: ");
Serial.print(icm20600.getGyroscopeX());
Serial.print(", ");
Serial.print(icm20600.getGyroscopeY());
Serial.print(", ");
Serial.print(icm20600.getGyroscopeZ());
Serial.println(" dps");
ak09918.getData(&x, &y, &z);
x = x - offset_x;
y = y - offset_y;
z = z - offset_z;
Serial.print("M: ");
Serial.print(x);
Serial.print(", ");
Serial.print(y);
Serial.print(", ");
Serial.print(z);
Serial.println(" uT");
// roll/pitch in radian
roll = atan2((float)acc_y, (float)acc_z);
pitch = atan2(-(float)acc_x, sqrt((float)acc_y*acc_y+(float)acc_z*acc_z));
Serial.print("Roll: ");
Serial.println(roll*57.3);
Serial.print("Pitch: ");
Serial.println(pitch*57.3);
double Xheading = x * cos(pitch) + y * sin(roll) * sin(pitch) + z * cos(roll) * sin(pitch);
double Yheading = y * cos(roll) - z * sin(pitch);
double heading = 180 + 57.3*atan2(Yheading, Xheading) + declination_shenzhen;
Serial.print("Heading: ");
Serial.println(heading);
Serial.println("--------------------------------");
delay(500);
�
99void calibrate(uint32_t timeout, int32_t *offsetx, int32_t *offsety, int32_t*offsetz)
100{
101 int32_t value_x_min = 0;
102 int32_t value_x_max = 0;
103 int32_t value_y_min = 0;
104 int32_t value_y_max = 0;
105 int32_t value_z_min = 0;
106 int32_t value_z_max = 0;
107 uint32_t timeStart = 0;
108
109 ak09918.getData(&x, &y, &z);
110
111 value_x_min = x;
112 value_x_max = x;
113 value_y_min = y;
114 value_y_max = y;
115 value_z_min = z;
116 value_z_max = z;
117 delay(100);
118
119 timeStart = millis();
120
121 while((millis() - timeStart) < timeout)
122 {
123 ak09918.getData(&x, &y, &z);
124
125 /* Update x-Axis max/min value */
126 if(value_x_min > x)
127 {
value_x_min = x;
128
// Serial.print("Update value_x_min: ");
129
// Serial.println(value_x_min);
130
131
132 }
133 else if(value_x_max < x)
134 {
value_x_max = x;
135
// Serial.print("update value_x_max: ");
136
// Serial.println(value_x_max);
137
138 }
139
140 /* Update y-Axis max/min value */
141 if(value_y_min > y)
142 {
value_y_min = y;
143
// Serial.print("Update value_y_min: ");
144
// Serial.println(value_y_min);
145
146
147 }
148 else if(value_y_max < y)
149 {
value_y_max = y;
150
// Serial.print("update value_y_max: ");
151
// Serial.println(value_y_max);
152
153 }
154
�
155 /* Update z-Axis max/min value */
156 if(value_z_min > z)
157 {
value_z_min = z;
158
// Serial.print("Update value_z_min: ");
159
// Serial.println(value_z_min);
160
161
162 }
163 else if(value_z_max < z)
164 {
value_z_max = z;
165
// Serial.print("update value_z_max: ");
166
// Serial.println(value_z_max);
167
168 }
169
170 Serial.print(".");
171 delay(100);
172
173 }
174
175 *offsetx = value_x_min + (value_x_max - value_x_min)/2;
176 *offsety = value_y_min + (value_y_max - value_y_min)/2;
177 *offsetz = value_z_min + (value_z_max - value_z_min)/2;
178}
Note
There are 3 demos in the library:
test_6axis
This example shows how to get gyroscope and acceleration data from ICM20600.
test_magnet
This example shows how to get magnetic data from AK09918.
compass
This example gets magnetic data and acceleration data, to count pitch and roll, and
make a compass application.
Step 4. Upload the demo. If you do not know how to upload the code, please
check How to upload code.
Step 5. Open the Serial Monitor of Arduino IDE by click Tool-> Serial Monitor. Or
tap the Ctrl + Shift + M key at the same time. Set the baud rate to 9600.
�
Success
If every thing goes well, when you open the Serial Monitor, the notice will pop up--Start
figure-8 calibration after 2 seconds. Which means in order to calibrate this module, you
should move it and draw the number 8 trajectory in the air. When the "......." appears,
you can start your calibration.
1Start figure-8 calibration after 2 seconds.
2.......................................................................
3A: -362, -205, 738 mg
4G: -45, 12, -1 dps
5M: -6, -23, -33 uT
6Roll: -15.53
7Pitch: 25.30
8Heading: 23.99
9-------------------------------10A: -269, 583, 61 mg
11G: 102, 377, -2 dps
12M: 18, -21, -18 uT
13Roll: 84.03
14Pitch: 24.65
15Heading: 215.58
16-------------------------------17A: -495, 229, 37 mg
18G: -43, -231, 201 dps
19M: 7, -30, 6 uT
20Roll: 80.83
21Pitch: 64.90
22Heading: 21.76
23--------------------------------
Note
As you can see, the result of compass example includes three parameter: roll, pitch and
Heading. There are the terminology of Euler angles(click to check more information).
Fuction table
Function
Description
ICM20600
initialize()
Initialize the chip LCM20600, by default:
the measurement range of gyroscope is ±2000 dps
the measurement range of accelerometer is ±16g
setGyroScaleRange(gyro_scale_type_t
range)
After the initialization, you can set the gyroscope range to meet your
own needs, the parameter gyro_scale_type_t range list:
RANGE_250_DPS
RANGE_500_DPS
RANGE_1K_DPS
�
Function
Description
RANGE_2K_DPS
e.g.
icm20600.setGyroScaleRange(RANGE_1K_DPS);
this code line will change the gyroscope measurement range to
±1000dps
setAccScaleRange(acc_scale_type_t range) After the initialization, you can set the accelerometer range to meet
your own needs, the parameter acc_scale_type_t range list:
RANGE_2G
RANGE_4G
RANGE_8G
RANGE_16G
e.g.
icm20600.setAccScaleRange(RANGE_8G);
this code line will change the accelerometer measurement range to
±8g
getGyroscope(int16_t* x, int16_t* y,
int16_t* z))
You can use this function to get the gyroscope X/Y/Z 3‐axis data at the
same time, and the unit of the data is dps
getGyroscopeX(void)
getGyroscopeY(void)
getGyroscopeZ(void)
Or, you can get the gyroscope X/Y/Z 3‐axis data separately by using
those three functions, and the unit of the data is dps
getRawGyroscopeX(void)
getRawGyroscopeX(void)
getRawGyroscopeX(void)
Those three functions get the raw data directly from the register of
ICM20600 without convert the data unit to dps
getAcceleration(int16_t* x, int16_t* y,
int16_t* z)
You can use this function to get the X/Y/Z 3‐axis acceleration at the
same time, and the unit of the data is mg
getAccelerationX(void)
getAccelerationY(void)
getAccelerationZ(void)
Or, you can get the X/Y/Z 3‐axis acceleration separately by using those
three functions, and the unit of the data is mg
getRawAccelerationX(void)
getRawAccelerationY(void)
getRawAccelerationZ(void)
Those three functions get the raw data directly from the register of
ICM20600 without convert the data unit to mg
getTemperature(void)
You ca use this function to get the temperature
�
Function
Description
AK09918
getData(int32_t *axis_x, int32_t *axis_y,
int32_t *axis_z)
You can use this function to get the magnetic force of 3‐axis.
Project
This is the introduction Video of this product, simple demos, you can have a try.
Tech Support
Please do not hesitate to submit the issue into our forum.
http://wiki.seeedstudio.com/Grove‐I2C_UV_Sensor‐VEML6070/ 11‐5‐18
�